Due to the coronavirus pandemic, vaccines have been the burning topic. It seems that it is the only thing the world has been talking about for months now. Sure, we have all got shots before, but the truth is that those vaccines have been administered for years.
Did you ever think about how a vaccine is manufactured? Yes, it is a lengthy process, and to be frank, it is quite interesting. Because of this, in the following article, we will introduce you to some of the main manufacturing steps that occur.
How long does it take?

The first thing that we will discuss is the length of this process. Nevertheless, we have to make something clear. There is a big difference between a production process of a vaccine that is already created and creating one from scratch.
When it comes to the former, it mainly depends on numerous factors, but generally speaking, one batch that includes a couple of thousands of doses can be manufactured in two to six weeks. This is true only if the vaccine has been tested and approved.
On the other hand, when it comes to creating one from scratch, it can take years because a lot of research has to be conducted. Firstly, scientists have to gather all information about the disease they are targeting. Then, they have to consider how it is transmitted and what symptoms it causes. Plus, there are multiple stages of inspecting and testing its effects.
Finding the antigen
We have already stated that the entire process of making a vaccine takes a lot of time, and understanding what antigen they should include is one of the initial steps scientists take. It is the main ingredient of every vaccine that exists nowadays. Basically, an antigen is a compound that will trigger your immune system’s response. It can be anything that your body doesn’t recognize, such as a protein or even a virus and bacteria in their weakened form. Upon introducing it to the system, your body will start fighting it since it is an unknown substance, and this way, you will eventually become immune to it.
Decreasing its power
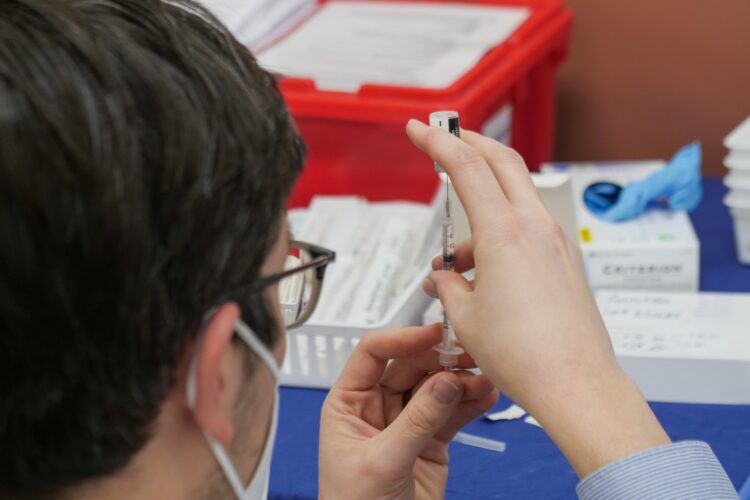
When it comes to this step, there are two options – either the weakened virus is used or the inactive one. For the former option, the scientists change its blueprint. In normal circumstances, viruses multiple thousands of times during the infection period, but when it comes to the vaccines, it only happens fewer than 20 times. Yes, the virus will still be present in your body upon getting the shot, but it won’t be as nearly as powerful, which means that it cannot cause the disease. The main advantage of those that use weakened virus is that one or two shots will enable you to become immune to it for the rest of your life, in most cases.
On the contrary, people who already have a weakened immune system can still be in danger when an active compound is introduced into their body, which is why there are also vaccines that include the inactive virus, that is, the one that has been killed by certain chemicals. The mere presence of it will trigger your immune system, but there is no risk of the virus doing any damage.
What are the other ingredients?
As already explained, the antigen is the main compound of every vaccine, but there are also other ingredients that enhance the response of your immune system. First of all, there are stabilizers that ensure no chemical reactions happen. Depending on the type of vaccine, some may be used on more than one recipient. In these situations, a preservative such as 2-phenoxyethanol is used to prevent them from being contaminated.
Then, there are residuals that are used during the manufacturing process. Naturally, these depending on the manufacturer, but according to Ology Bioservices, these may include antibiotics, yeast, or egg protein. Keep in mind that these aren’t active ingredients and that they occur in small quantities. Other ingredients include surfactants, adjuvant, and diluent.
What are the three phases of testing?
As you surely know, these are three phases of testing that a vaccine must pass before being approved. These occur after the antigen has been determined and the formula has been tested on animals. If it causes an immune response, the first phase begins. During the first phase, it is administered to volunteers. They are young people with a clean bill of health, and as you can assume, only a small number of people get it during this initial stage.
In the second phase, the number of people who get the shot is increased. When choosing volunteers, one of the main requirements is that they are of the same age and sex as the group from phase one. In addition, a group of people doesn’t get the vaccine, but they are still included in this stage to confirm whether the changes have occurred due to the efficiency of the shot or by chance.
In the final stage, the third phase, the vaccine is administered to thousands of people in multiple countries. Now, it is time to investigate whether it will be efficient when people from different backgrounds and lifestyles are included. During this phase, people who don’t get the shot are also included, but interestingly, neither they nor the scientists are aware of this fact. Only upon the testing has been concluded do they learn whether they go the real product or not. This is done with the goal of ensuring there are no external influences from the doctors and patients.
Review of findings
Once the clinical trial period is over, officials in each country go over all the findings and data to determine whether it should be approved. Naturally, it has to meet numerous important requirements before it gets authorized, and the manufacturing can begin. This is the main reason why it is so hard to develop a new vaccine. Many of them are promising during the first phase but then fail to meet the necessary requirements during the other two stages.
The distribution
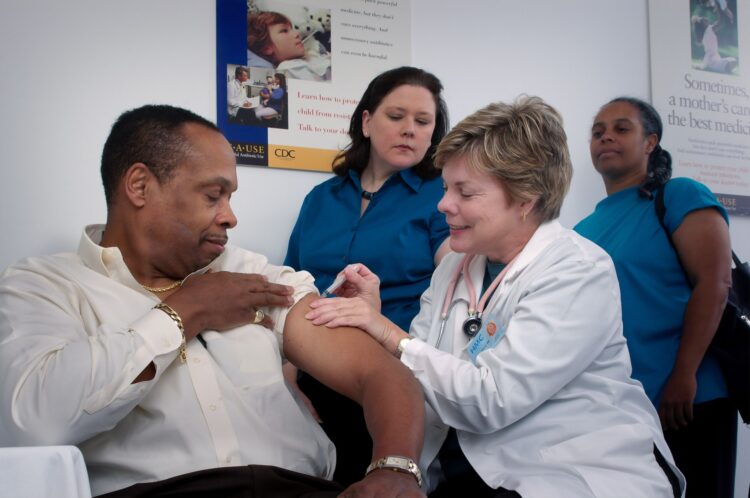
Even though some people might believe that the complex part is over since the vaccine has been made, there are still numerous requirements that have to be met. Firstly, syringes and vials that contain the formula must be designed according to the law of each country. Since it can greatly differ, a single shot won’t always be packed in the same way. This is also another step that must be authorized by officials before the vials are made available to the public.
Finally, the shipment is also determined by numerous specifications, and the most important one states that the vials have to been kept in cold surroundings (between 2°C and 8°C) to preserve their quality. The shipment process can take between two and four weeks depending on the location of the lab that produces them and the final stop, i.e., the country that ordered them.
 Hi Boox Popular Magazine 2024
Hi Boox Popular Magazine 2024



